Renowned for its ancient history, rich culture, and sensational landscapes, Turkey is dominated by highly favored destinations that draw millions upon millions of visitors annually.
Throughout its history, Turkey’s background and culture have been influenced by numerous cultures, such as Armenians, Romans, and Greeks. The country was a part of the Ottoman Empire, which ruled over numerous nations across Asia, Europe, and Africa for six centuries.
From hot air balloon rides widespread across social media to exploring the misty mountains of Eastern Black Sea, Turkey offers a wide variety of things to do. But that’s not all to check out in this unique country!
The considerable archaeological finds in Turkey, like the Lycian tombs, make it a hot spot for history buffs and inquisitive minds intrigued by ancient history. Other tourist attractions in Turkey include the dome and minaret filled skyline of Istanbul and the beaches along the Mediterranean. This is a country waiting to be explored!
In this post, we'll cover:
26. Ani Ruins
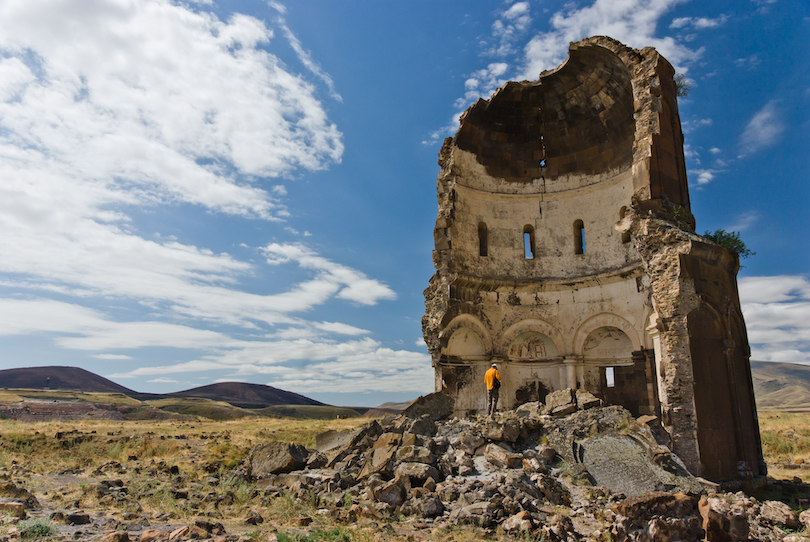

Across the Akhurian River from Armenia, the Ani Ruins are the remains of what once was the metropolis of Ani, an ancient Armenian city.
Established over 1,600 years ago, Ani was widely known as “the city of a thousand and one churches.” The walled city protected more than 100,000 residents in the 11th century, prosperous for its time. Unfortunately for the city, it was conquered, harassed, and attacked more than a few times resulting in Ani being utterly abandoned by the 1700s.
The Ani Ruins feature more than 30 caves, 50 churches, and 20 chapels, with other excavations discovering more of these historic structures. Reaching the Ani Ruins, the first sight is welcomed by towering city walls that have mostly stood tall and proud over the years.
Then, once past the walls, is one of the most favored structures preserved in the Ani Ruins, the Cathedral. It is the largest standing building in Ani, a domed basilica with pointed arches and cluster piers admired as the sun peeks through parts of its missing structure.
25. Duden Waterfalls, Antalya
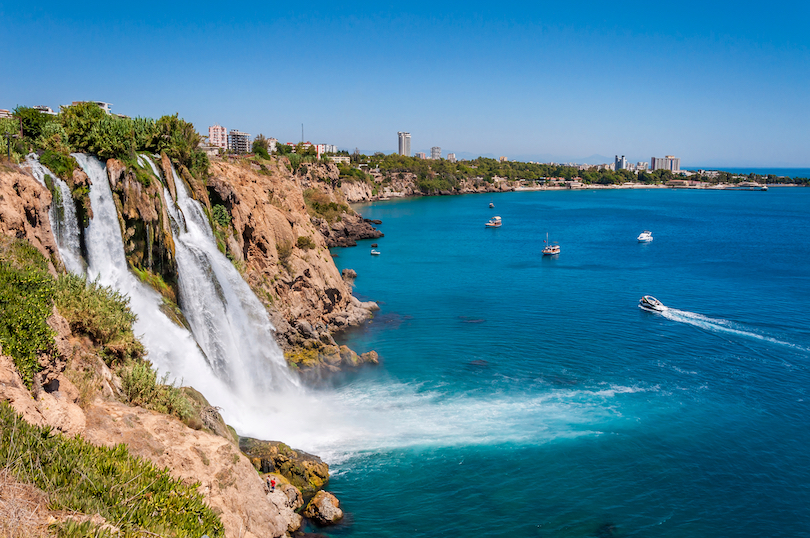

A collection of waterfalls in Antalya, the Duden Waterfalls pour into the rich turquoise waters of the Mediterranean Sea. The Duden Waterfalls are divided into Upper Duden Waterfall and Lower Duden Waterfall.
Upper Duden Waterfall, also referred to as Alexander Falls, is a favored recreational area, exuding a natural and refreshing charm surrounded by fresh greenery. The story goes that Alexander the Great allowed his horses to drink water here as he passed through the region. Behind the Upper Duden Waterfall are caves where people go to see the views of the flowing waterfall from below.
The Lower Duden Waterfall, also called Karpuzkaldiran Selalesi (which translates to watermelon raising waterfall), is found in the Lara District in Duden Park. The stunning scenery of the waterfall is often viewed by boat, the nearby sidewalk, or from Duden Park for those searching for a replenishing display of nature’s beauty and power. Lower Duden Waterfall drops water from Duden River, one of the largest in southern Anatolia, into the sea below.
24. Göbekli Tepe
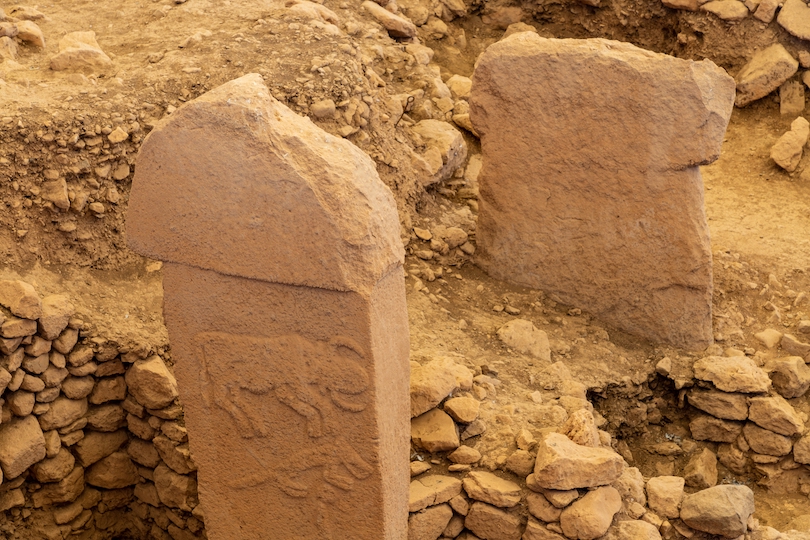

Dating back to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, Göbekli Tepe, translating to “Potbelly Hill,” is a famed archaeological site where the world’s oldest known megaliths were discovered. The megaliths are older than Stonehenge by about 6,000 years!
Discovered in the Germus Mountains, northeast of Sanliurfa, the archaeological site boasts the discovery of structures built by hunter-gathers estimated from 9,600 to 8,000 BCE and are assumed to be related to rituals of some sort.
The Sanliurfa Museum presents an impressive collection of artifacts excavated from Göbekli Tepe. Visitors can easily explore the site at Göbekli Tepe, the world’s oldest temple. Observe archaeologists at work as they excavate the enormous site that still offers up more monumental archaeological and historical finds. There’s a small museum at Göbekli Tepe where visitors can peer at intriguing 3D animations of the site and discover more about this impactful historical site.
23. Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, Ankara
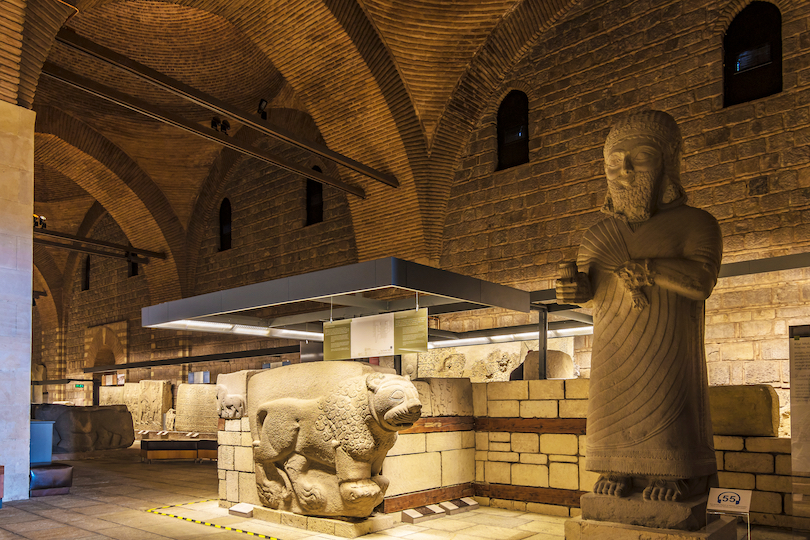

On the south portion of Ankara Castle in the capital of Turkey is the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, located in two Ottoman-aged buildings.
The Museum of Anatolian Civilizations is the perfect place to learn the complexity of Turkey’s background through top-class exhibits featuring original artifacts from various native archaeological sites. A journey through the museum’s exhibits, organized chronologically for ease of learning, takes visitors through different periods displaying impressive artifacts like the museum’s cuneiform tablets, which date back to 2 BC.
Peer at carved stone slabs from the 8,000-year-old archaeological site of Arslantepe, an ancient city. Gaze at horse bits and shields established by Anatolia’s leading metalworkers, the Urartians. There is so much to see and learn at the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations to comprehend the ancient history of Turkey.
22. Lycian Tombs in Fethiye
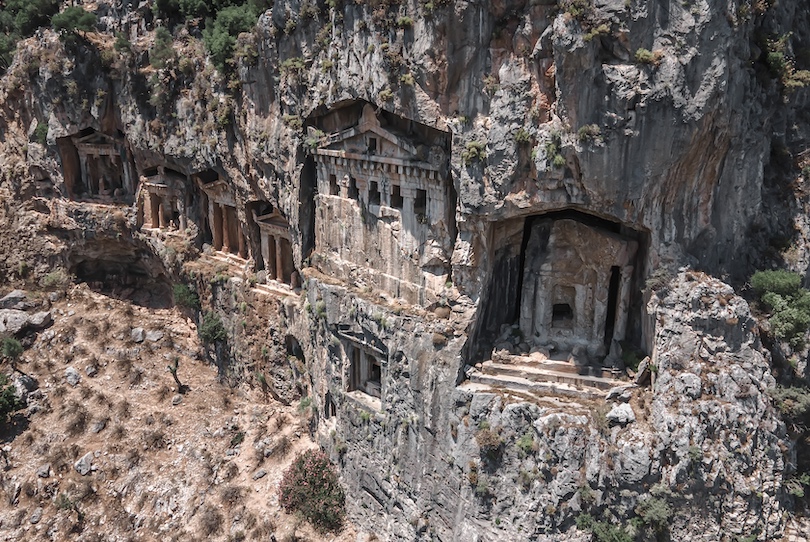

Discovered in Fethiye, the ancient Lycian Tombs were established for kings and queens. They are an architectural wonder dating back to around 350 BC, having been built in the side of a mountain to overlook the city of Fethiye below.
The Lycians were the people that lived in Lycia, a prosperous state bordering the Mediterranean Sea, from around 1400 BC to 546 BC. The Lycians believed that the dead were taken to the afterlife by winged creatures. The location of the Lycian Tombs in the cliffside was to have the honored dead closer to heaven.
Taking a river cruise to see the tombs is one of the most popular things to do in Turkey. The entryways of the Lycian Tombs in Fethiye are illuminated by towering Classical columns, the inside comparatively bare thanks to years of looters emptying the tombs.
21. Mardin Old Town
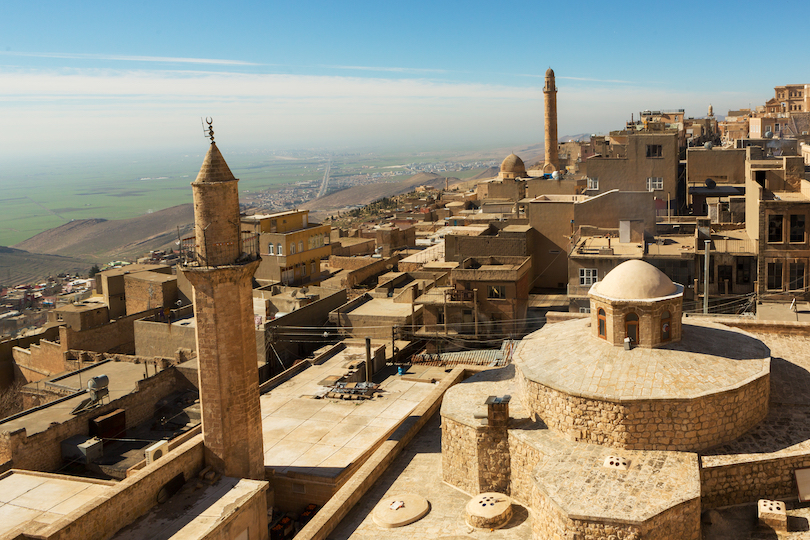

Near the Mesopotamian plains and north of the Syrian border, Mardin is a historical city full of spectacular architecture and thousands of years of intriguing history.
There are many fascinating things to do within Mardin’s Old Town, such as visiting the Mardin Museum in the ancient town square. The museum presents outstanding exhibits on the cultures established in Mardin throughout its history. Mardin Castle, commonly called Eagle’s Nest, overlooks the whole of Mardin, dating back 3,000 years.
The Mardin stone houses are another, featuring eye-catching Arab-style architecture strategically positioned, in a stair-like method, to overlook the plains of northern Syria and to prevent the houses from blocking each other’s view.
These stone houses enrich the atmosphere of the historic area. They draw in visitors from all over to get lost sightseeing in Mardin Old Town’s streets, surrounded by spectacular architecture and authentic design.
20. Grand Bazaar, Istanbul
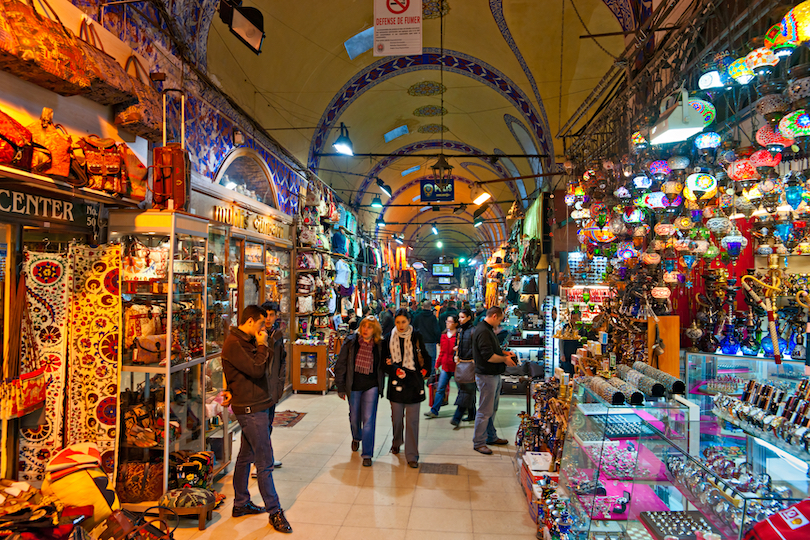

One of the world’s oldest and largest covered markets, the Grand Bazaar in Istanbul attracts hundreds of thousands of visitors daily.
Getting its start in 1461 during Ottoman rule, the bazaar continued to expand throughout the years to establish itself in its notoriety today. It’s one of the top tourist attractions in Istanbul, so you don’t want to miss a trip to this famed market and one of its famous sales, traditional hand-loomed carpets paired with a notorious storytelling experience from the seller.
The notorious Grand Bazaar boasts more than 4,000 stores, a police station, multiple banks and cafes, a post office, and a mosque. Scour the maze of the Grand Bazaar’s shopping paradise for traditional textiles, historical antiques, magic lanterns, Turkish rugs, and other unique finds. It’s not hard to spend hours walking through this historic and culturally rich market!
19. Uludag National Park
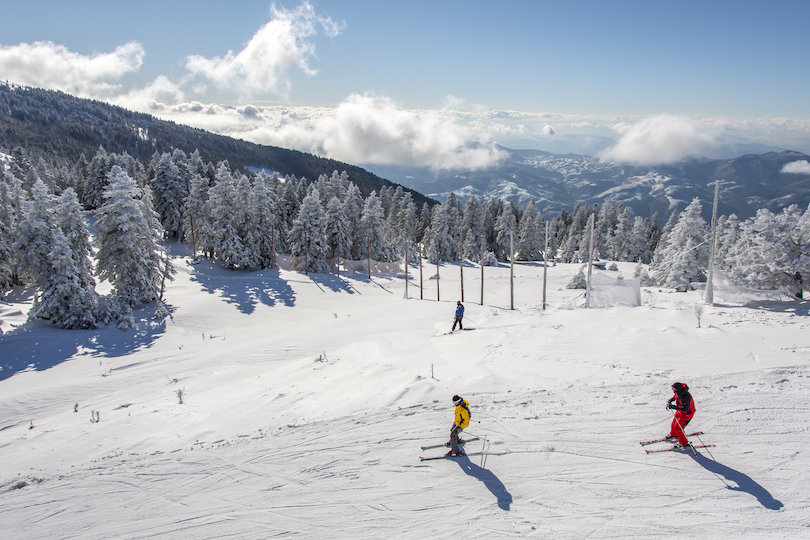

Near Istanbul and Bursa, Uludağ National Park is home to Mount Uludag, or Great Mountain, the highest point in the Marmara region. Known in ancient times as Olympos Misios, better known as Mount Olympus, the mountain where Zeus and other gods and goddesses were believed to have lived in mythology.
One of the premier destinations for winter sports and summer activities, Uludağ National Park, welcomes more than a million visitors annually. The world’s longest cable car, Uludağ Teleferik, connects the city of Bursa to Uludağ National Park and the nearby ski resort for visitors to take on the glorious landscapes of Mount Uludag.
Skii, hike, and explore the natural wonders of Uludağ National Park. Watch for its numerous endemic species of plants and animals. Then, walk to the secluded Softabogan Waterfall, where locals and tourists swim and relax in nature. Finally, join fellow skiers on the slopes, weaving down the mountainside surrounded by fir trees and snow.
18. Pergamon Acropolis
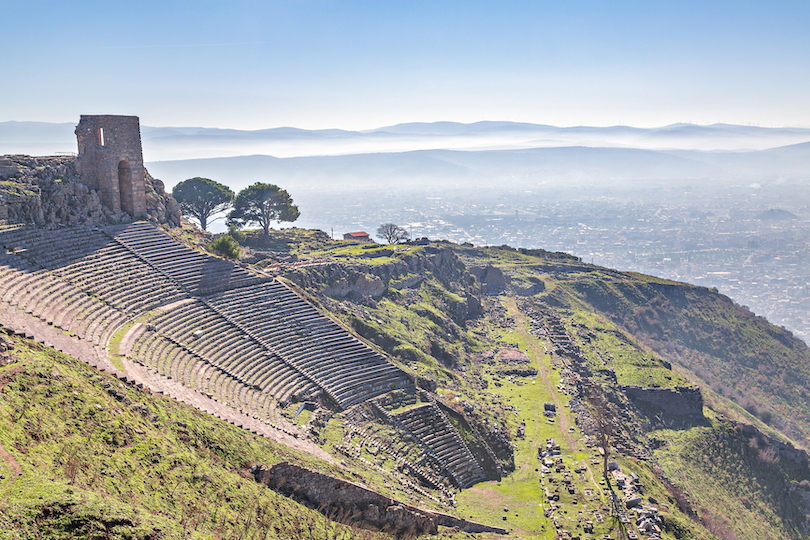

Pergamon was once an ancient and wealthy Greek city. Now, the Acropolis of Pergamum rests atop a hill facing the town center of Bergama.
The archaeological site of the acropolis is one of the most reputed in Turkey. Impressive temples and a picturesque theater are scattered across the ancient ruins. However, one of the most well-known points of interest at the Pergamon Acropolis is the marble-columned Temple of Trajan, the only Roman monument on the site.
It was built under the order of the Roman emperor Trajan and was completed by Trajan’s successor, Hadrian. The purpose of the Temple of Trajan was to act as a place for others to worship the rulers and Zeus, along with strengthening the relationship of Rome with the people of Pergamon. Other enigmatic historical structures at Pergamon Acropolis include the Hellenistic theatre, the Temple of Dionysus, and the Altar of Zeus.
17. Ruins of Troy
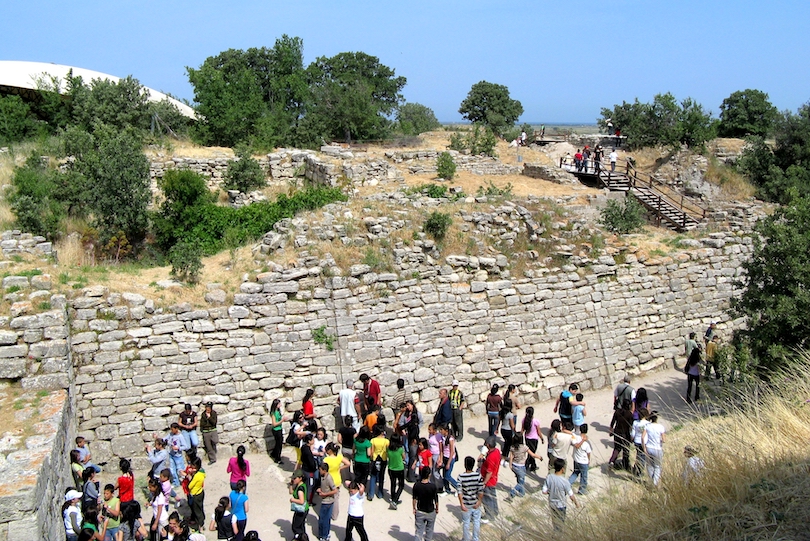

The legendary city of Troy may not be left standing, but its ruins are open for exploration for a giant leap back to the time of the tales of the great Trojan War and the Trojan Horse.
Troy’s tale was written by Homer in The Iliad, detailing the story of the famed Achilles and the siege that ended in the Trojans losing the war to the Greeks. However, what was previously believed to be a myth was discovered in 1870 after an archaeologist uncovered the city of Troy.
The Ruins of Troy are found on the Turkish Aegean coast, near the village of Tevfikiye. The site has been established as a famous tourist attraction, featuring a walk through the ruins, a Trojan Horse model, and the Troy Museum. The museum preserves and exhibits archaeological finds from the city of Troy and nearby sites.
16. Side
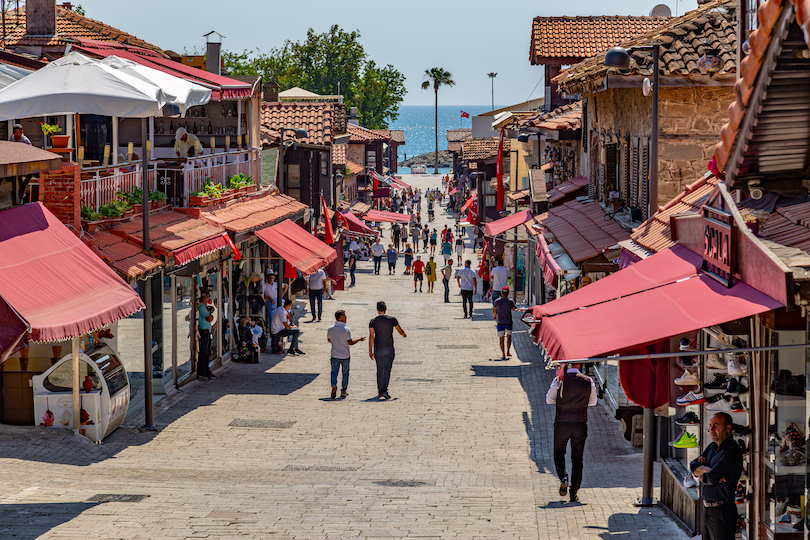

Settled on the southern Mediterranean coast, between Alanya and Antalya, Side is a stunning city drawing in visitors with its impressive ancient ruins, renowned resorts and plenty of things to do.
An ancient port city, Side’s natural charm combines a paradise of sunshine and sandy beaches with the impact-fullness of ancient architecture and archaeological sites. The city’s origins date back to 7 BCE, quickly becoming a significant trading post of the region. Throughout history, the city fell under the rule of many leaders and cultures that have impacted Side, including Alexander the Great.
Explore the ancient Roman-style theater that hosted gladiator fights in Side’s Old Town, which dates back to 2 AD. Peer through the Side Archaeological Museum’s significant collection of ancient artifacts sourced from Side and other nearby excavation sites.
Or turn the tides and head down to Side’s turquoise beaches for a day spent relaxing in the sun and basking in nature. Then head to Side’s Old Town market for Turkish goods, including jewelry and clothing, to bring home souvenirs!
15. Topkapi Palace
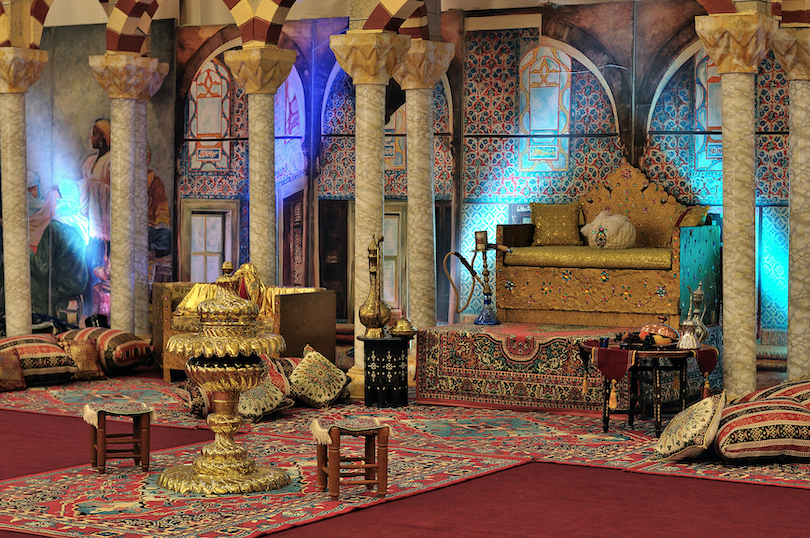

Found in the Fatih district in Istanbul, the Topkapi Palace served as the residence for sultans until the 17th century. It is now a grand museum displaying the grandeur of Turkey’s history and wealth.
Topkapi Palace was established in the 15th century under the order of Sultan Mehmed II. Once the Ottoman Empire’s reign failed in 1923, the palace was restructured into a museum, becoming a famous tourist attraction for visitors to see and imagine the life of sultans. The museum welcomes more than three million visitors a year.
Visitors can observe the remarkable exhibitions that display kaftans, portraits, sacred relics, and the world’s fifth-largest diamond, the Spoonmaker’s Diamond. Through the Harem section, which served as the private residence of the sultans and their concubines, are handmade Iznik tiles of the finest quality. And that’s only some of the stunning beauty of the Topkapi Palace, with its grand courtyards, prosperous gardens, and intricate architecture.
14. Goreme Open-Air Museum
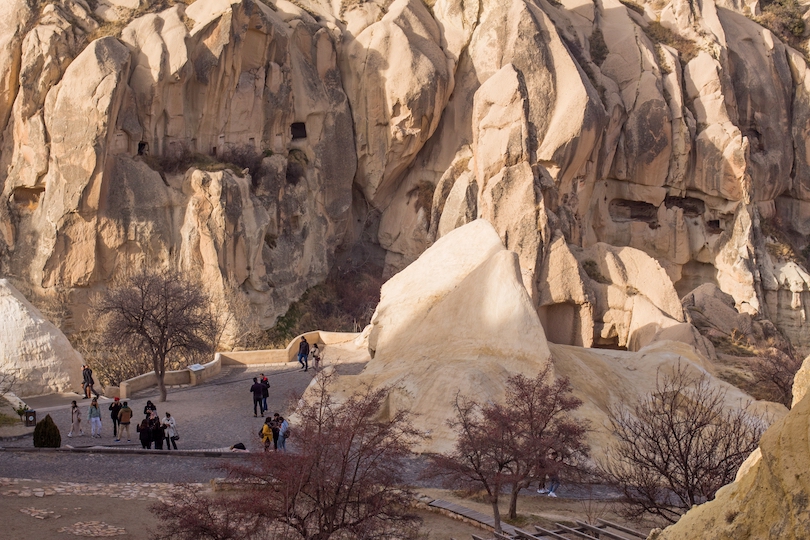

Located in Cappadocia, the Goreme Open-Air Museum preserves a collection of intricate rock-carved churches, many dating back to the 10th-12th centuries. The churches prospered under the direction of one of three prominent Cappadocian Fathers, Saint Basil of Caesarea, who played a vital role in the advancement of early Christian theology.
Many of these early churches exhibit stunning displays of Byzantine art that adorn the ceilings and walls, imagining scenes from the Bible, which aided followers who were unable to read. Elmali Kilise, or Apple Church, is one of the well-known churches within the Goreme Open-Air Museum. This church dates back to around 1050, with art depicting numerous frescoes of Biblical scenes, like The Last Supper.
13. Bodrum Castle
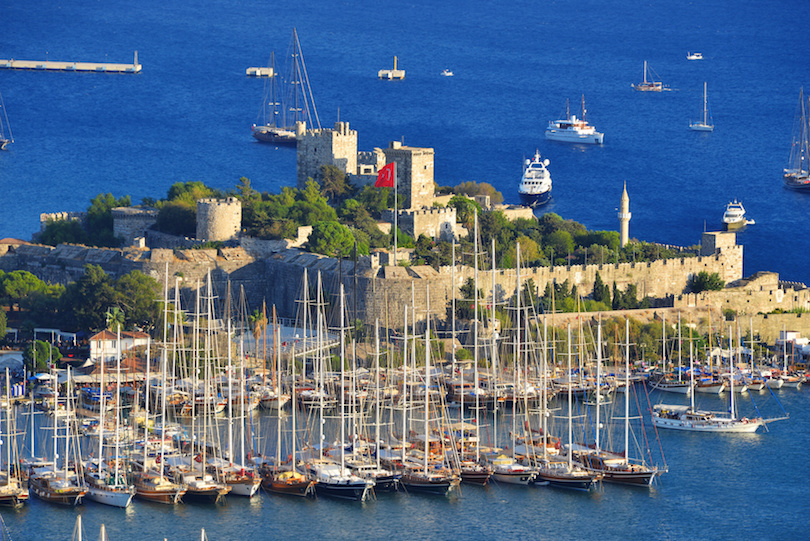

Fortified on a rocky peninsula on the southwest coast, Bodrum Castle, also known as the Castle of St. Peter, was built by Crusader knights in the 15th century as protection against the Seljuk Turks. The castle now is a popular sight in Bodrum, housing the world-famous Museum of Underwater Archaeology, which features significant underwater finds from shipwrecks and historical civilizations.
Bodrum Castle’s walls are well-preserved, paired with imposing towers and turrets that exude an enigmatically medieval and fairytale-like feeling. A step into the time of knights patrolling the castle, fending off invaders, the castle served as a refuge for Christians in Asia Minor.
Each of the castle’s four towers is named after the nations responsible for its construction: German, English, French, and Italian towers. After the Ottomans overtook the castle under the reign of Suleyman the Magnificent, the castle was re-established as a prison in 1895.
12. Kaymakli Underground City
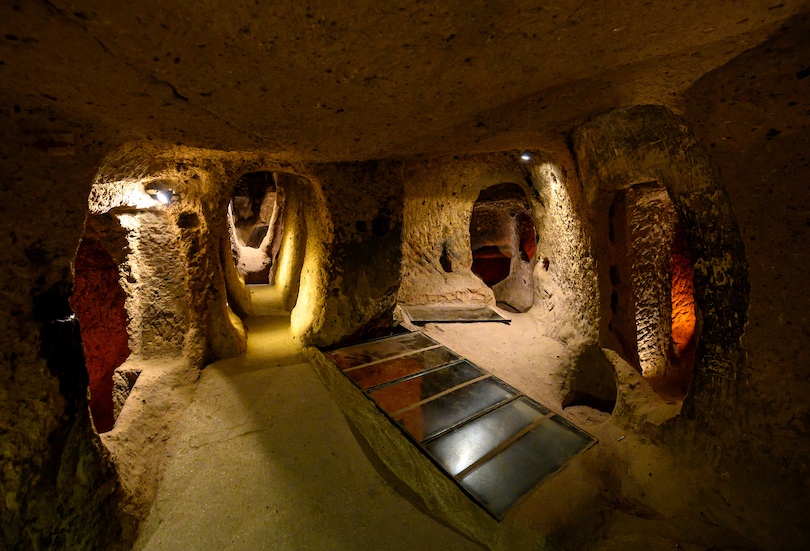

Within the citadel of Kaymakli, near Nevsehir, the Kaymakli Underground City is one of the most famed underground cities, believed to have been established around 2,000 BCE.
In ancient times, the underground city was called Enegup. Over time, it served as a shelter for those seeking refuge during the Arab-Byzantine wars, the underground city expanding to become the widest in Turkey.
Only the first four of the eight levels are open to the public. The floors closer to the surface were where the wealthier families resided. Walking through Kaymakli Underground City, you’ll note kitchens, homes, stables, and a church, imagining how ancient settlements resided in the maze of one of Cappadocia’s oldest underground cities.
11. Patara Beach
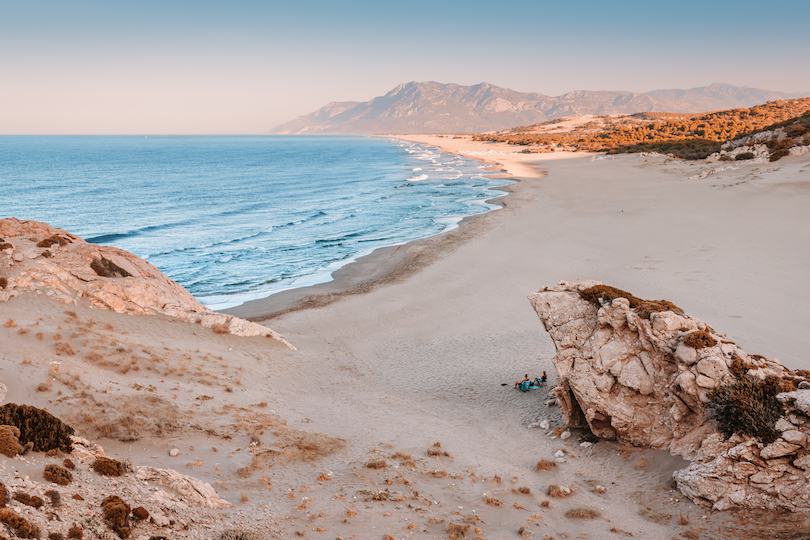

The widest and longest beach in Turkey, Patara Beach, is decorated with yellow sand dunes and refreshing views near the ancient Lycian town of Patara. The town was the birthplace of St Nicholas, the 4th-century Byzantine bishop who later passed into legend as Santa Claus.
Patara Beach is a famous beach and tourist attraction, its honey-yellow sand resembling a desert more than a beach. The surrounding area is undeveloped, offering a desirable location for peace, and if you time it right, you can experience the magical views as the sunset falls beneath the waterline.
Inland from the beach are ancient Lycian and Roman ruins. So, make a day of exploring and enjoying the best of Patara. Soak in the sand and the breeze at Patara Beach and visit the ancient Patara ruins, including the necropolis and basilica, to get the best of both worlds!
10. Lake Van
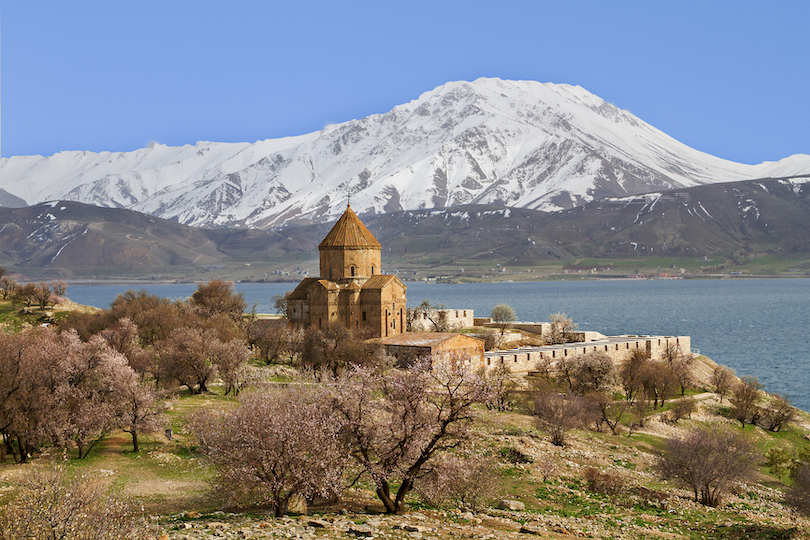

The second largest lake in the Middle East and the largest in Turkey, Lake Van, lies near the border of Iran.
Known as Arsissa Lacus or Thospitis Lacus in ancient times, the lake was created by a volcanic explosion of Mount Nemrut. Near the southern section of Lake Van are four small islands, all of which have been designated important archaeological sites. One of the islands, Akdamar Island, is a popular tourist attraction thanks to its preserved Church of the Holy Cross and other monastery ruins that date back to the 10th century.
Under the waters of Lake Van was a surprising discovery of an underwater castle. Archaeologists and scholars are still in deep discussion over this accidental find. Still, it truly empowers the rich history of Turkey – home to thousands of years of history, culture, and stories.
9. Sumela Monastery
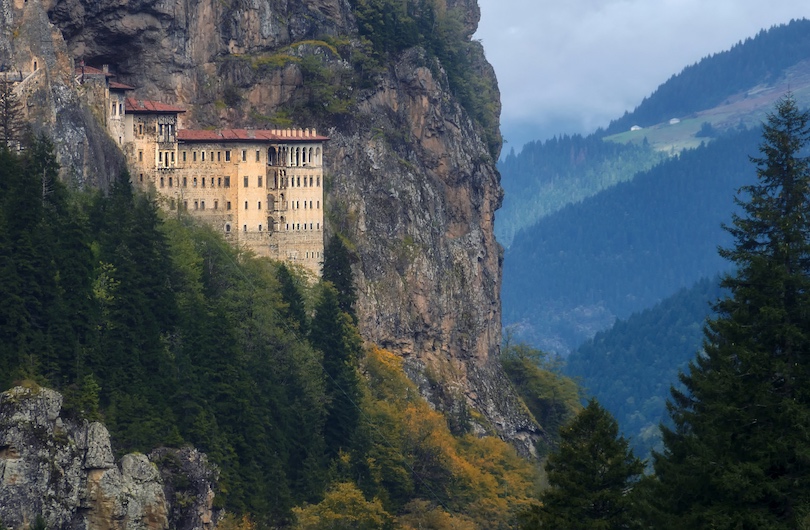

Balancing confidently on the cliffside of Mela Mountain within the Pontic Mountains, the Sumela Monastery is an ancient Orthodox monastery built in the 4th century. The monastery was abandoned in 1923, becoming an established museum and beloved tourist attraction.
Throughout the Sumela Monastery and museum are breathtaking frescoes dating back to the 18th century. These ancient depictions feature biblical scenes like Jesus Christ and the Virgin Mary.
The surrounding scenery of the Sumela Monastery, paired with the hike over to the location, is stunning. From foggy days casting a serene solitude to the atmosphere and sunny days that clear the fog to present awe-inspiring views of the mountains or waterfalls dotting the way, the Sumela Monastery is settled in the perfect location to revel in nature and history.
8. Olüdeniz
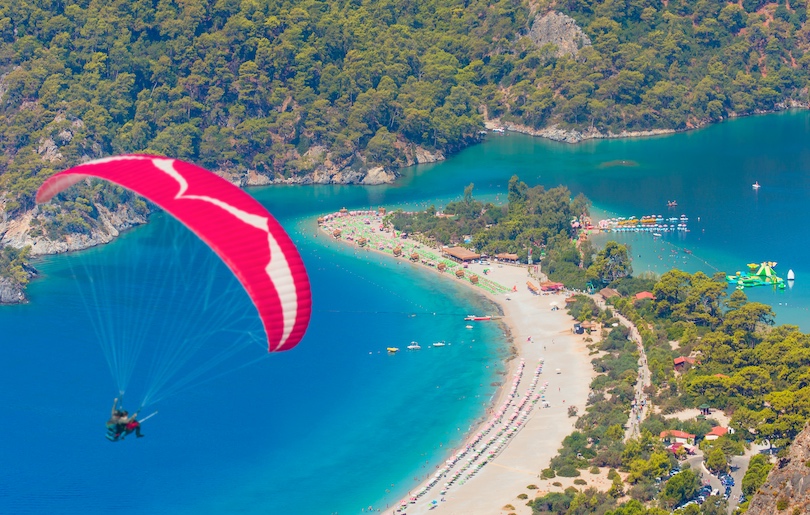

Famous for its stunning blue lagoon, Olüdeniz is a village and resort town established on the southwest coast of Turkey.
Spend a few days unpacking the numerous activities waiting to be experienced at this breathtaking destination. Paragliding above Olüdeniz is one of the most popular things to do with unreal viewpoints of the mountains and blue sea all around you.
Then, check out the most famous and photographed attraction of Olüdeniz–the Blue Lagoon! A national conservation site, the lagoon’s calm waters are ideal for swimming, kayaking, paddle boarding, and snorkeling.
Go for a dive or learn how to at the numerous educational diving schools for a unique adventure in Olüdeniz’s archaeological diving sites. Then, join a boat trip to the nearby famous Blue Cave, with its piercing blue colors and foundation created by limestone rock.
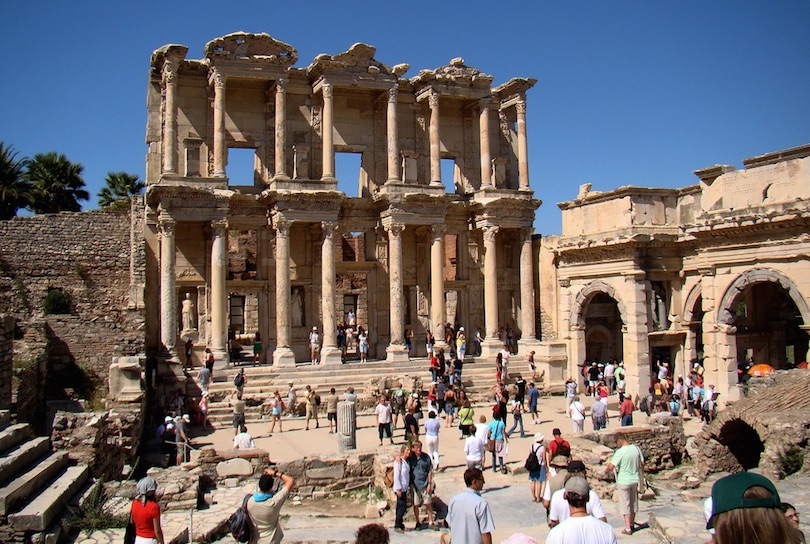
7. Ephesus
An ancient city near Selcuk, Ephesus was once a wealthy metropolis and capital of the Eastern Roman Empire. It was established around one of the Seven Wonders of the World, the Temple of Artemis.
The city’s origins begin in 4 BCE, founded by one of Alexander the Great’s military generals, Lysimachos. Along with its numerous ruins are the Basilica of St. John, the House of the Virgin Mary, and the Mosque of Isa Bey. Other iconic historical attractions include the Great Theater and the Library of Celsus.
The Great Theater dates back to the Hellenistic era, re-structured by the Romans to become Ephesus’s three-story amphitheater, social hub, and site for gladiator fights. The Library of Celsus was built by a prominent member of the Roman Senate, Tiberius Julius Celsus Polemaeanus. It was one of the largest Roman libraries of its time, featuring a grand arched entrance and Corinthian columns.
6. Aspendos Theater
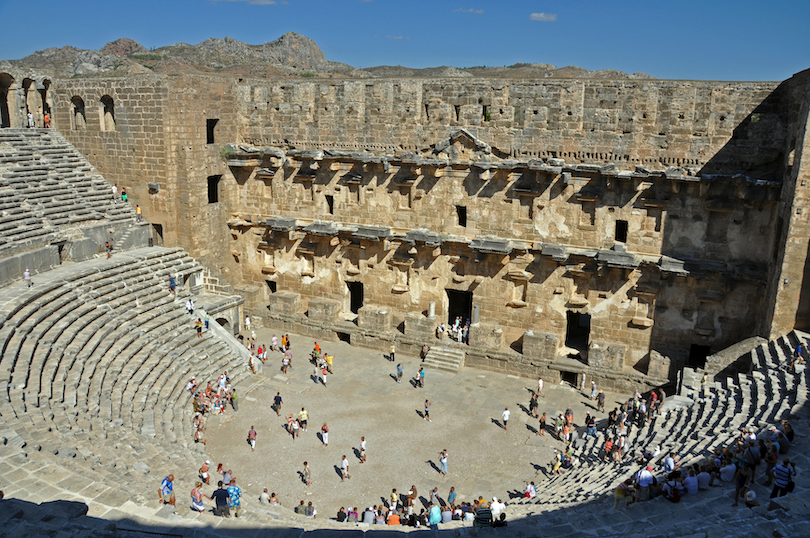

Not far from Antalya is the ancient city of Aspendos and its famous historical landmark and tourist attraction, the Aspendos Theater.
The Aspendos Theater is one of the best preserved ancient theaters of antiquity, constructed during the Roman emperor Marcus Aurelius’s reign. Its sheer size is remarkable, exuding the wealth and prosperity of its ancient city.
The theater could seat between 15,000 and 20,000 spectators. Because the stage area was later used as a caravanserai (a roadside inn) in Seljuk times, it was continuously repaired and maintained.
Today the Aspendos Theater is used for its original purpose again, hosting the Aspendos International Opera and Ballet Festival annually, showing off the theater’s outstanding acoustics and intricate architectural design.
5. Pamukkale
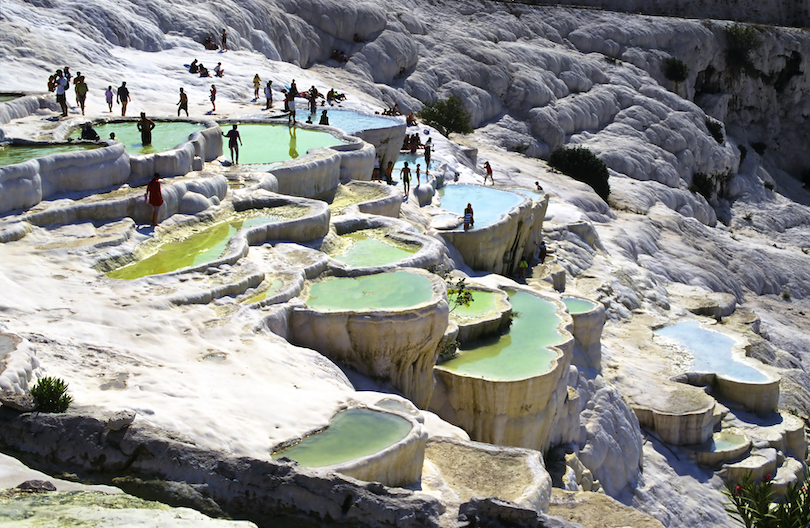

Pamukkale, meaning “cotton castle” in Turkish, is an unreal landscape in western Turkey, famous for its white terraces and. The terraces are made of travertine, a sedimentary rock deposited by water with a very high mineral content.
People have bathed in its pools for thousands of years. The ancient Greek city of Hierapolis was built on top of the hot springs by the kings of Pergamon.
A natural wonder, these rock formations formed beneath the ancient city of Hierapolis transform into a cascading water fountain. The water is sourced from ancient hot springs that helped form the shell-shaped terrace pools over millennia.
Above Pamukkale’s stunning white travertine pools is the famous attraction Cleopatra’s Antique Pool. The pool in which Cleopatra herself once swam, this pool features warm and clear water surrounded by Roman ruins, including fallen columns and carved stones to explore.
4. Blue Mosque
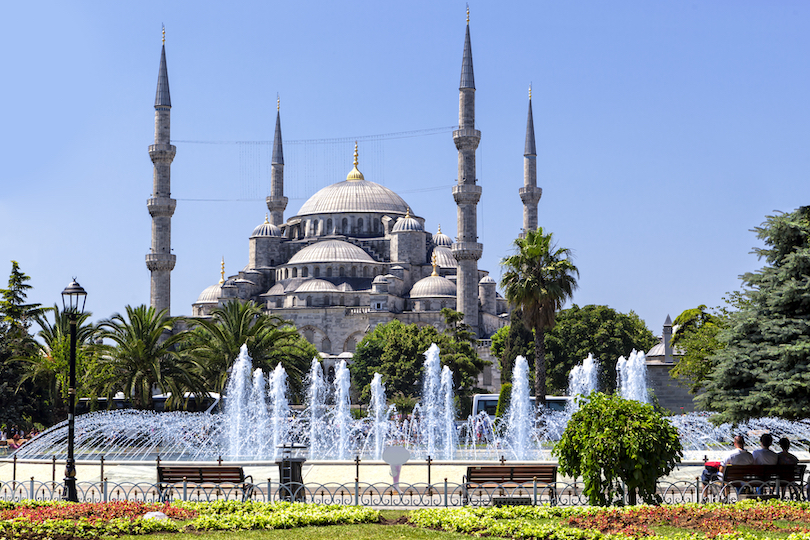

Known officially as the Sultan Ahmed Mosque, the Blue Mosque of Istanbul is a famous attraction that lures many tourists throughout the year.
The colossal and majestic architectural beauty of the Blue Mosque is an attraction itself, established next to the famous Hagia Sophia. The Blue Mosque is a testament to the Ottomans’ achievements and wealth throughout history, the only mosque with six minarets in Istanbul.
Built in the early 16th century, the Blue Mosque is known for its interior’s blue walls, totaling 20,000 blue tiles. It is an active place of worship and is open to the public except during prayer, which lasts 90 minutes.
3. Mount Nemrut
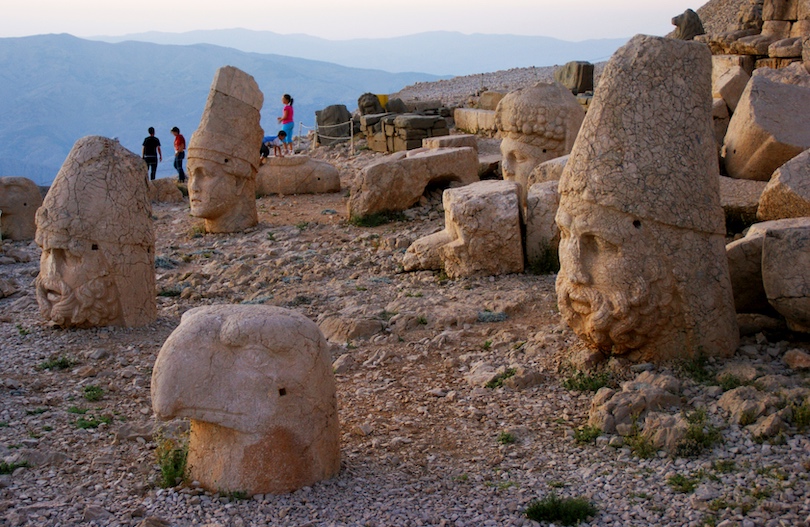

One of the highest peaks in the Eastern Taurus Mountains, Mount Nemrut is famous for homing the funerary mound of King Antiochus I of the Kingdom of Commagene at its peak.
Commagene was an ancient Armenian kingdom, eventually incorporated into the Roman empire in 72 AD. King Antiochus I was the most famous ruler of the kingdom. The funerary mound features sculptures of the king, other gods, lions, and eagles. The king decreed the funerary mound’s dedication so that he was to be deified and worshiped as the other gods depicted on the stones.
Since their construction, the heads have toppled from the bodies and lay scattered throughout the site. The summit of Mount Nemrut provides a great view of the surrounding mountains. The main attraction is to watch the sunrise from the eastern terrace which give the bodyless heads a beautiful orange hue and adds to the sense of mystery of the place.
2. Hot Air Balloon Ride in Cappadocia
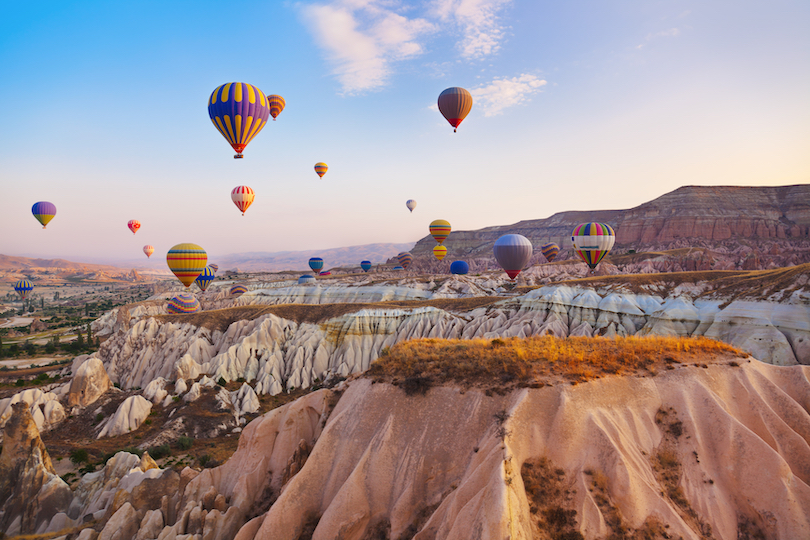

One of the best places in the world for hitching a scenic hot air balloon ride, Cappadocia is famous for its picturesque 360-degree viewpoints of sprawling valleys and weird natural rock formations.
Southeast of Ankara, the region of Cappadocia is home to big tourist towns such as Goreme and Urgup. As a result, its hot air balloon season is open year-round. Before sunrise, 100 hot air balloons are permitted to take off, and then after that, 50 more are granted permission after every half hour after sunrise – so make sure you’re on time for your hot air balloon reservation!
This is one of the most things to do in Turkey. Make sure you book your hot air balloon trip early, so you don’t miss out on this one-of-a-kind adventure!
1. Hagia Sophia
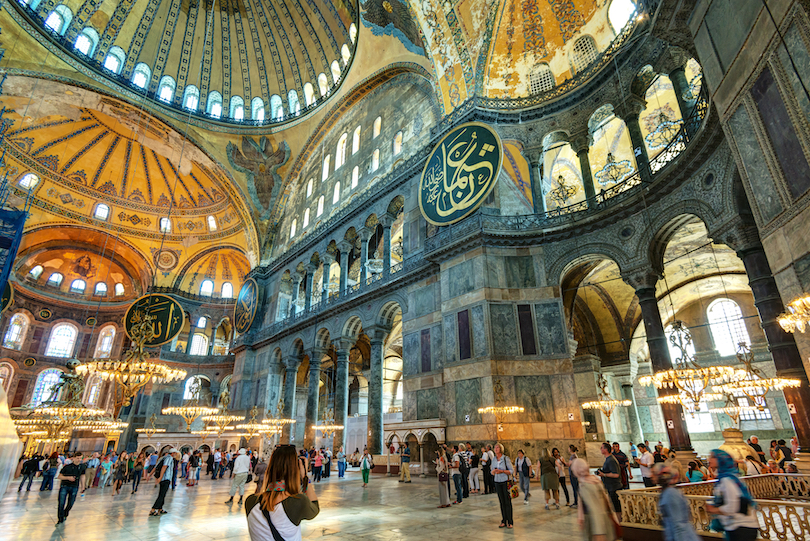

Located next door to the Blue Mosque in Istanbul, the Hagia Sophia was originally a basilica constructed for the Eastern Roman Emperor Justinian I in the sixth century. A masterwork of Roman engineering, the massive dome (31 meters or 102 feet in diameter) covers what was for over 1000 years the largest enclosed space in the world.
The church was looted by the fourth Crusaders in 1204, and became a mosque in the 15th century when The Ottomans conquered the city. The Hagia Sophia was converted into a museum in 1935 and is now one of the top attractions in Turkey.
The public can now absorb the architectural marvels of Hagia Sophia, which translates to “Holy Wisdom.” Throughout Hagia Sophia are columns and marble sourced from ancient city ruins in Syria and Anatolia, such as the pink marble from Afyon. Unique mosaics decorate the walls of Hagia Sophia, like the VI Leon mosaic Pantaktrator Jesus on the Emperor’s Gate. The gate’s origins date back to the 6th century and were only used by the Emperor.
Map of Tourist Attractions in Turkey
 © OpenStreetMap © MapTiler © Touropia
© OpenStreetMap © MapTiler © Touropia











Regarding the theatre at Aspendus: if it was built in AD 155, then it was erected during the reign of the Emperor Antoninus Pius (r. AD 138-161). (Perhaps your source was Wikipedia, which also erroneously lists Marcus.)